WordPress powers a massive portion of the internet, making it a fantastic platform for creators, businesses, and bloggers. However, its popularity also makes it a prime target for hackers. A hacker that compromises a WordPress website can damage your business reputation, lose customer data, and destroy your hard work overnight.
But don’t worry. Securing your WordPress site doesn’t require you to be a cybersecurity expert. By following these essential security techniques provided by RankYa, you can build a strong defence against hacking of your online temple “your WordPress site”.
Video Tutorial for Securing WordPress Site
Use Strong, Unique Passwords and Manage Users Wisely
This is the first line of defence. A weak password is like leaving your front door unlocked. A brute-force attack is an automated attempt by hackers to guess your password over and over again.
- Use Strong Passwords: Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Example of a strong password N^ii9j6&S@6giE.Ft5psQGL%& that is hard to crack.
- Unique is Key: Never reuse your WordPress password on other sites. Use a password manager (e.g. Google Password Manager) to keep track of your login details and passwords.
- Limit Admin Access: Not everyone needs to be an administrator. Assign users appropriate role they need to do their job (e.g., Editor, Author). Delete any old or unused user accounts.
- Disable User Registration: If you do not operate a membership site, disable user registration feature. Go to WordPress > Settings > General > Membership and UNCHECK Anyone can register and SAVE Changes.
Keep Everything Updated. Always
Outdated software is the #1 reason WordPress sites get hacked. Vulnerabilities are regularly discovered in the WordPress core, themes, and plugins. Updates almost always contain critical security patches.
Sample WordPress Codes
WordPress Core: Major releases often require a thorough backup before you update. Place the next code in wp-config.php for automatic updates of WordPress Core.
define('WP_AUTO_UPDATE_CORE', true);
Below code can be placed within wp-config.php. It will disable the ability for logged in Administrator to update WordPress Core, Plugins and Themes through WordPress Dashboard (simply comment out of remove this line of code when you are ready for major update).
define('DISALLOW_FILE_MODS', true);
Plugins and Themes: This is crucial. Hackers often target popular plugins with known security vulnerabilities. Check for updates every time you log in and apply them promptly. Delete any plugins or themes you are not actively using.
Place this in your Theme functions.php for automatic updates of plugins
add_filter( 'auto_update_plugin', '__return_true' );
Place this in your Theme functions.php for automatic updates of your active theme
add_filter( 'auto_update_theme', '__return_true' );
Important Considerations
While enabling automatic updates can be convenient for website maintenance and security, it can sometimes lead to conflicts or even break your WordPress site if an update has compatibility issues. Always ensure you have a recent, reliable backup of your website before enabling automatic updates for plugins and themes.
Install a Reputable Security Plugin
A good security plugin is like having a dedicated security guard for your website. It actively scans for malware, monitors for suspicious activity, and can block attacks before they even reach your site. Install and use one of these popular security plugins:
- Wordfence Security: Offers a robust firewall and malware scanner. Furthermore, the default settings are great for most WordPress site installations. RankYa recommends WordFence.
- Sucuri Security: Provides comprehensive security monitoring, auditing, and hardening.
- iThemes Security: A great option with a wide range of features to lock down your site.
Implement Regular Backups
Sometimes, despite your best efforts, things can go wrong. A reliable backup is your ultimate safety net. If your site is ever compromised, you can restore a clean version and get back online quickly.
Don’t rely on your hosting provider’s backups alone. Either manually backup (content, database and at least wp-content folder), or use a dedicated WordPress backup plugin like UpdraftPlus or Jetpack Backup to schedule automatic backups and store them in a secure location like your local computer,Google Drive or Dropbox.
Better Protect Your phpMyAdmin Database
Often overlooked aspect of WordPress Security is MySQL® Database User Credentials. When a WordPress site is not manually installed, default phpMyAdmin user passwords are often weak and can be updated to be more complex and secure.
Often overlooked aspect of WordPress Security is MySQL® Database User Credentials. When a WordPress site is not manually installed, default phpMyAdmin user passwords are often weak and can be updated to be more complex and secure. You can always change it through cPanel MySQL® Databases settings.
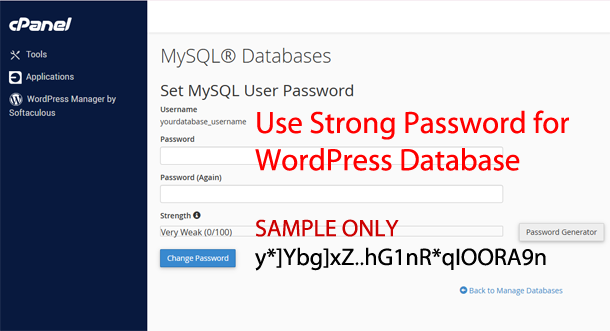
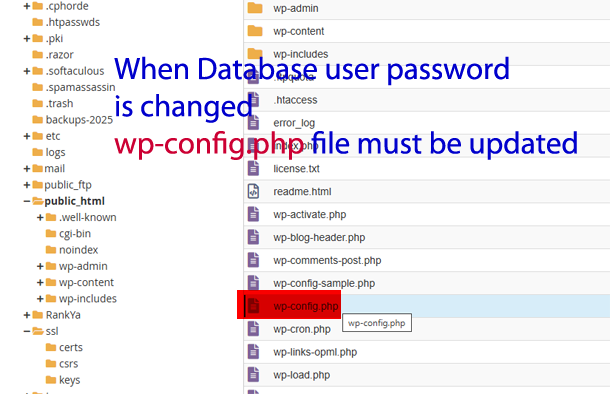
Important: If you change Database Password, you must update wp-config.php file to include the new password.
Furthermore: Not ALL MySQL® Database User Privileges are needed for most WordPress Installations. For most setups, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, and ALTER permissions are good enough. You can change these settings through cPanel MySQL® Databases Manage User Privileges.
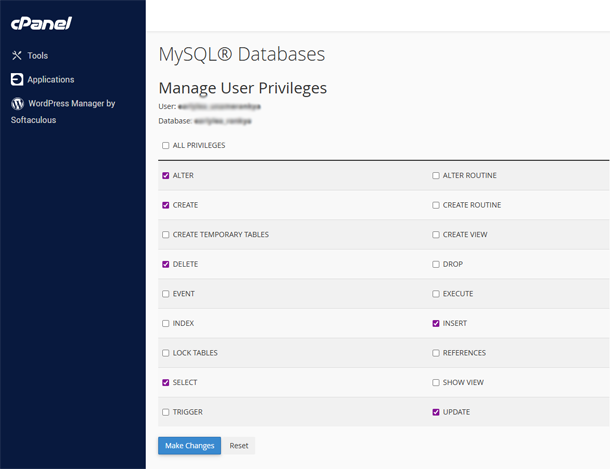
NOTE: While WordPress primarily uses these permissions for standard operations, some plugins or themes might require higher privileges such as DROP, EXECUTE (or others) for their error free functionality.
Use an SSL Certificate (HTTPS)
An SSL certificate encrypts the data transferred between your website and your visitors’ browsers. This is essential for protecting login credentials and any personal information submitted on your site. Google also views HTTPS as a positive ranking signal, and modern browsers will flag sites without it as “Not Secure.”
Most reputable hosting providers now offer free SSL certificates (often from Let’s Encrypt). Check your hosting control panel to ensure it’s activated for your domain.
Choose Quality Web Hosting
Your hosting provider is the foundation of your website’s security. A cheap, low-quality host might cram thousands of sites onto a single server with poor security configurations. A good host invests in a secure infrastructure, offering server-level firewalls, malware scanning, and knowledgeable support. RankYa recommends Crazy Domains.
Sample WordPress .htaccess Security Directives
WordPress installations need special codes to function. All installations will have .htaccess inside the main installation directory. You can add additional security directives to better protect your WordPress site. .htaccess mod_rewrite security directives for WordPress (.txt format).
You can also browse in to wp-content > UPLOADS folder and create a seperate .htaccess file to include more directives. .htaccess directives for protecting WordPress Uploads Folder (.txt format).

Website Security is an Ongoing Process
Website security isn’t a “set it and forget it” task. It’s an ongoing process of vigilance and maintenance. By integrating these proven best practices into your regular WordPress management routine, you can reduce the security risk and ensure that your WordPress site remains a safe, secure, and successful platform for years to come.
